As regenerative medicine evolves, two platelet-based procedures have taken the spotlight: PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) and PRF (Platelet-Rich Fibrin). Both harness the body’s own blood to accelerate healing, rejuvenate skin, and stimulate hair growth — yet they are not the same.
To deliver consistent clinical results, it’s essential to understand how PRP and PRF differ — not only in preparation but in composition, release profile, and therapeutic effect.
Let’s break down the science behind these two platelet concentrates and how your choice of tube and centrifugation method can make or break results.
What Are PRP and PRF?
PRP (Platelet-Rich Plasma) is a plasma fraction containing a high concentration of platelets — usually 2–5 times higher than baseline blood levels. Platelets are packed with growth factors that accelerate tissue regeneration, collagen formation, and angiogenesis.
PRF (Platelet-Rich Fibrin), on the other hand, is a second-generation concentrate that doesn’t rely on anticoagulants. Instead, it uses the body’s natural clotting process to form a fibrin matrix that traps platelets and releases growth factors slowly over time.
Both are derived from the patient’s own blood — but the tube composition, centrifugation speed, and presence or absence of anticoagulant lead to very different outcomes.
Key Differences in Preparation and Tubes
The most defining difference between PRP and PRF lies in how they’re processed.
| Feature | PRP | PRF |
|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulant | Yes (usually ACD) | No |
| Tube Composition | Tube with ACD + gel | Plain glass or silica-coated tube |
| Centrifugation Speed | High (3,000–4,000 rpm) | Low (1,000–2,000 rpm) |
| Plasma Type | Liquid plasma | Fibrin clot |
| Growth Factor Release | Immediate | Sustained (up to 7–10 days) |
PRP tubes typically contain ACD-A anticoagulant and a separation gel. When centrifuged, red blood cells settle at the bottom, gel in the middle, and plasma on top. This plasma layer is then extracted for injection or topical use.
- Tube type: PRP tubes contain anticoagulant (ACD/sodium citrate) and a separating gel.
- Process: Blood is centrifuged to isolate platelet-rich plasma.
- Application: Injected into the target area or applied with microneedling.
Common PRP Applications:
- Hair restoration (androgenic alopecia)
- Facial rejuvenation (“PRP facials”)
- Scar treatment and skin texture improvement
- Joint pain, sports injuries, and musculoskeletal healing
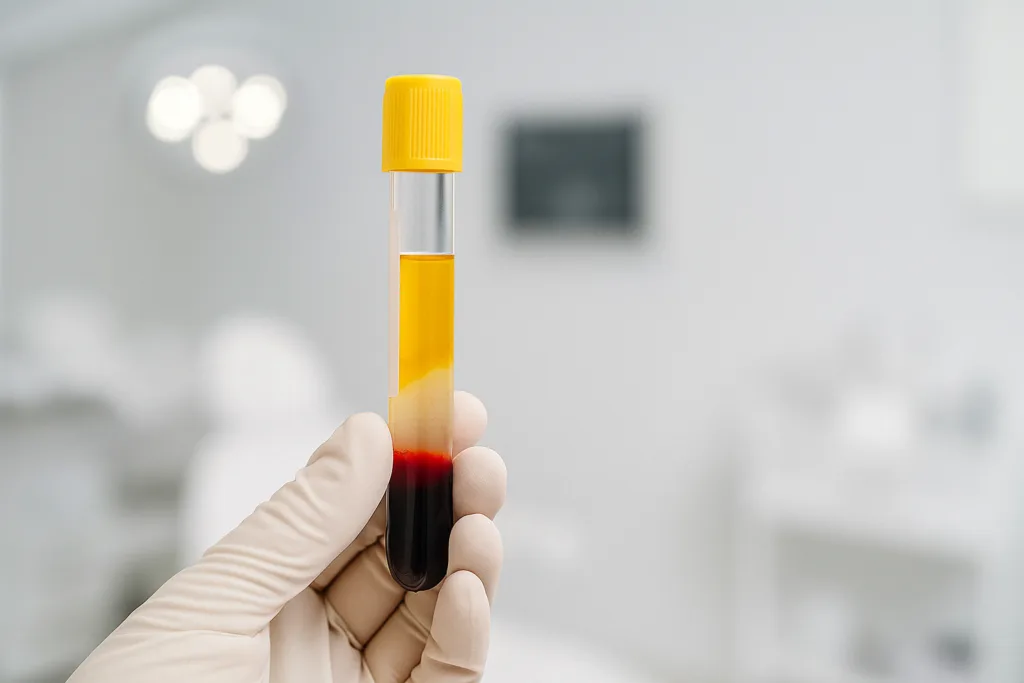
PRF tubes contain no anticoagulant — this means clotting begins as soon as blood enters the tube. The centrifugation must start immediately at a lower speed to form a soft fibrin matrix rich in platelets and leukocytes.
The right choice depends on your treatment goals:
• For precision injections and hair restoration, PRP’s liquid form is ideal.
• For wound healing and dermal rejuvenation, PRF’s slow-release fibrin works better.
- Tube type: PRF tubes are additive-free (no anticoagulant). Some contain a natural gel separator.
- Process: Blood is centrifuged at higher g-force, forming a fibrin clot enriched with platelets and leukocytes.
- Application: Applied as a membrane or injected into treatment areas.
Common PRF Applications:
- Dental implantology and bone grafting
- Oral surgery and periodontal regeneration
- Chronic wound healing
- Under-eye rejuvenation and skin tightening
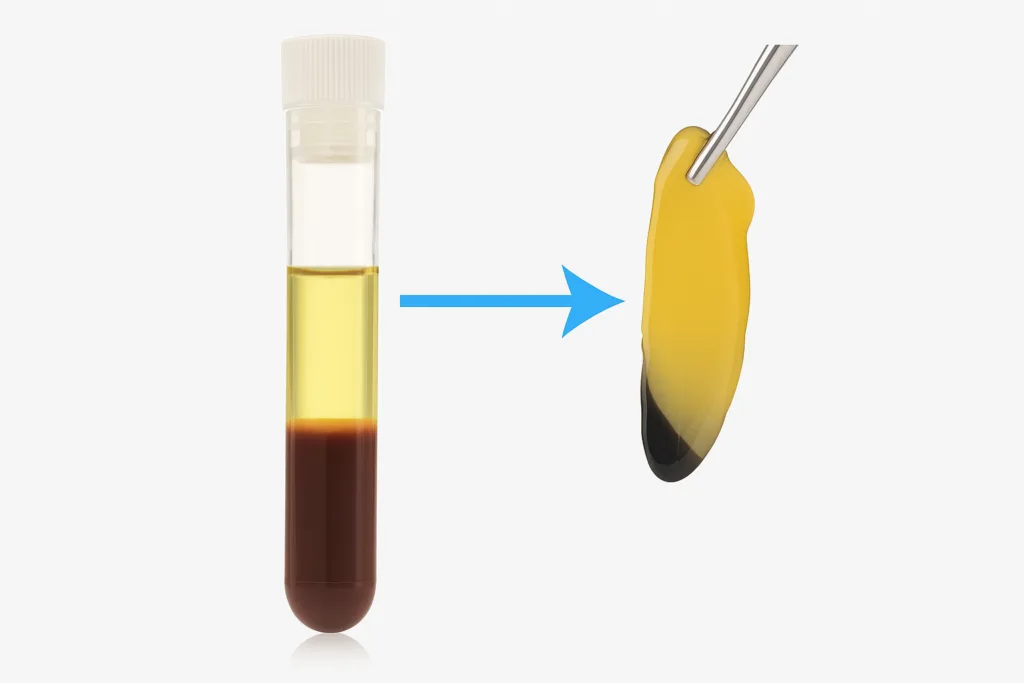
The Science Behind Platelet Activation and Fibrin Formation
In PRP
ACD prevents clotting during preparation. Activation happens only when the PRP is injected into the tissue or combined with calcium chloride or thrombin. This gives practitioners precise control over when platelets start releasing their regenerative factors.
Key growth factors released include:
- PDGF (Platelet-Derived Growth Factor) – stimulates fibroblast proliferation
- TGF-β (Transforming Growth Factor Beta) – enhances collagen production
- VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) – promotes new blood vessel formation
In PRF
Because PRF contains no anticoagulant, clotting begins instantly. Platelets become embedded in a fibrin matrix, which acts as a scaffold that slowly releases growth factors over several days.
This sustained release mimics natural wound healing — ideal for tissue repair, bone regeneration, and post-surgical applications.
PRP vs PRF Tubes: Key Differences for Clinics
| Feature | PRP Tubes | PRF Tubes |
|---|---|---|
| Tube Composition | Contains anticoagulant (ACD/sodium citrate) + separating gel | No anticoagulant, natural clotting forms fibrin matrix |
| Platelet Concentration | Higher platelet concentration | Moderate platelet concentration, but includes leukocytes |
| Growth Factor Release | Fast release, strong initial effect | Slow, sustained release over several days |
| Centrifuge Protocol | Lower g-force (typically 1200–1500 RPM, 8–10 minutes) | Higher g-force (up to 2700 RPM, 10–12 minutes, depending on tube) |
| Composition | Platelet-rich plasma with minimal fibrin | Platelet-rich fibrin matrix with leukocytes & cytokines |
| Applications (Aesthetics) | Hair restoration, facial rejuvenation, scar treatment | Under-eye rejuvenation, skin tightening, wound healing |
| Safety & Naturalness | Anticoagulant needed, higher preparation control | More natural, additive-free, lower infection risk |
| Best For | High platelet demand (hair restoration, joint repair, aesthetics) | Long-term regeneration (dentistry, wound healing, facial PRF) |

Platelet Concentration and Biological Effects
Both PRP and PRF aim to concentrate platelets, but the method affects their distribution and functionality.
| Parameter | PRP | PRF |
|---|---|---|
| Platelet Concentration | 3–5× baseline | 2–3× baseline |
| Leukocytes | Variable | High |
| Fibrin Matrix | None (liquid) | Present |
| Growth Factor Release | Short burst (within hours) | Gradual release (up to 7 days) |
In essence, PRP = immediate boost, PRF = sustained healing.
Clinicians often combine both in comprehensive treatment plans — PRP for short-term rejuvenation and PRF for long-term tissue support.
Tube Composition: ACD, Gel, and Glass/PET
The choice of tube directly influences plasma purity and platelet recovery.
PRP Tubes
A quality PRP tube includes:
- ACD Anticoagulant: Prevents clotting, maintaining platelet integrity.
- Separation Gel: Ensures a clean plasma layer.
- Vacuum Sterility: Prevents contamination and air exposure.
This setup produces a clear, concentrated plasma layer ready for extraction. The separation gel barrier makes it ideal for hair restoration, facial rejuvenation, and intra-articular injections.
When PRP Is Preferred
Doctors often recommend PRP therapy when:
- High platelet concentration is needed quickly
- Treating sports injuries, joint conditions, or hair loss
- Performing cosmetic facial rejuvenation, scar treatment, or microneedling with PRP
- Patients require strong short-term healing response
PRF Tubes
PRF tubes are plain glass or silica-coated, without anticoagulant. The silica particles activate clotting, allowing the fibrin to form.
However, not all glass tubes are suitable for medical use. Clinics must ensure that their PRF tubes are CE certified and made from biocompatible borosilicate glass, as lower-quality tubes can cause cytotoxic reactions or unpredictable clot formation.
IPPOCARE offers both PRP tubes (ACD + Gel) and PRF tubes (no anticoagulant), allowing practitioners to select based on procedure type and patient profile.
When PRF Is Preferred
PRF may be more suitable when:
- A long-lasting regenerative effect is needed
- Performing oral surgery, implantology, or bone grafting
- Patients prefer a natural, anticoagulant-free preparation
- Treating chronic wounds or delicate under-eye rejuvenation
Which Is Better for Skin vs Hair Treatments?
For Skin Rejuvenation
PRP is typically preferred for facial injections or microneedling because it provides:
- Smooth viscosity for even distribution
- Controlled platelet activation
- Immediate glow and collagen stimulation
PRF, however, can be advantageous in undereye, acne scar, and wound healing procedures due to its fibrin structure and sustained growth factor release.
For Hair Restoration
PRP remains the gold standard for scalp treatments. Its liquid form allows even diffusion through mesotherapy needles, and its high platelet concentration boosts follicular regeneration.
However, combining PRP and PRF — a method often called “hybrid PRP/PRF therapy” — can yield superior outcomes: PRP for initial stimulation and PRF for long-term nourishment.
| Clinical Goal | Recommended Type |
|---|---|
| Fine-line reduction, glow, rejuvenation | PRP |
| Hair loss, scalp regeneration | PRP |
| Acne scars, wound healing | PRF |
| Bone grafts, oral surgery | PRF |
| Combined regenerative therapy | PRP + PRF hybrid |
Some advanced clinics now use dual-spin protocols, collecting both PRP and PRF from the same patient in a single session — giving flexibility to customize for each treatment zone.
Choosing the Right Tube for Your Clinic
Both PRP and PRF therapies play important roles in regenerative medicine. The right choice depends on:
- Treatment goals (quick recovery vs sustained regeneration)
- Clinical specialty (aesthetics, dentistry, orthopedics)
- Patient preference (natural vs high-concentration therapy)
👉 At IPPOCARE, we provide a wide range of PRP tubes (Classic, Biotin, HA-enriched) and PRF tubes for doctors and clinics worldwide. Each tube is CE-certified, sterile, and optimized for platelet recovery to ensure safe and effective treatments.
| Factor | PRP | PRF |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation Time | 10–15 min | 5–8 min (must act fast) |
| Ease of Use | Easy to control | Time-sensitive |
| Consistency | Highly standardized | Variable (depends on timing) |
| Applications | Hair, face, joints | Wounds, bone, under-eye, scars |
| Additives Required | Anticoagulant (ACD) | None |
CE Certification and Safety Considerations
Regardless of whether you use PRP or PRF, tube certification is non-negotiable. The use of non-certified blood collection devices can result in contamination, inconsistent results, and regulatory violations.
CE-certified tubes ensure:
- Biocompatibility and sterility under ISO 13485 standards
- Proper vacuum calibration for exact blood volume
- Safe anticoagulant or activator dosage
Clinics should always verify documentation and choose suppliers with transparent testing data.
For reference, IPPOCARE’s Classic PRP Tube (ACD + Gel) and CE-certified PRP Tubes comply with ISO sterilization and quality requirements.
How Tube Choice Influences Results
The right tube design determines how many viable platelets and leukocytes are available for treatment.
- PRP tubes with ACD + gel ensure high yield and clean plasma.
- PRF tubes without additives ensure a natural fibrin network.
A substandard tube can trap platelets in the gel layer or trigger early clotting, wasting valuable plasma. Always use certified, medical-grade PRP and PRF tubes designed for clinical centrifugation.
PRP and PRF aren’t rivals — they’re complementary tools in regenerative medicine.
PRP offers precision and immediate biological activation; PRF provides structure and sustained healing. Together, they form a complete strategy for cellular repair, collagen remodeling, and long-term tissue health.
Understanding the science — and choosing the right CE-certified tube — allows clinics to achieve reproducible, high-quality outcomes for every patient.
- PRP provides high platelet concentration and rapid healing, making it ideal for aesthetics and sports medicine.
- PRF delivers a sustained, natural release of growth factors, making it valuable in dentistry, wound care, and delicate facial rejuvenation.
By stocking both tube types, clinics can provide customized treatment options that improve patient outcomes and build trust.
👉 Ready to equip your clinic?
Explore our full selection of PRP tubes and PRF tubes, CE-certified and trusted by aesthetic professionals worldwide.
🔗 Explore Related Products
PRF Tubes for Clinical Use
CE-Certified PRP Tubes
Classic PRP Tube (ACD + Gel)
FAQs About PRP and PRF Tubes
PRP uses an anticoagulant and remains in liquid form, while PRF is made without anticoagulant, forming a fibrin matrix for slow growth factor release.
Yes. Many clinics combine PRP and PRF to achieve both immediate and sustained regenerative effects.
Yes. PRP tubes contain ACD or sodium citrate to prevent clotting, allowing proper platelet separation during centrifugation.
PRF is considered more natural since no anticoagulant is used, but both are safe when prepared with sterile, certified tubes.
PRP is generally preferred due to its higher platelet concentration, though PRF may be used for supportive regeneration.
It depends on your specialty and patient needs. For facial aesthetics and hair restoration, PRP tubes (with or without HA) are ideal. For oral surgery and wound healing, PRF tubes are recommended.
PRP tubes with a separating gel allow for clear plasma separation during centrifugation, resulting in higher platelet recovery and cleaner plasma for injections. Tubes without gel may lead to contamination with red or white blood cells, making them less suitable for consistent clinical use. Most modern PRP tubes for professional use include both gel and anticoagulant (ACD) for optimal platelet yield.
PRP and PRF tubes are commonly available in 8mL, 10mL, or 12mL sizes. For facial treatments or small-area injections, 8–10mL tubes are usually sufficient. For hair restoration or orthopedic procedures, doctors often prefer 10–12mL tubes to ensure enough plasma volume is collected. The choice of tube size depends on the treatment area and required platelet concentration.
No. PRP and PRF tubes are single-use, sterile medical devices. Reusing tubes increases the risk of infection and violates medical safety standards. Always dispose of used tubes in a proper biohazard container according to hospital and clinic regulations.
📅 Last Updated: November 2025